Index
Introduction
The Relevance of Understanding Kidney Nodules
Kidney nodules are changes that can occur in the kidneys and, although they do not always represent a severe condition, can cause concern when identified. Understanding what a kidney nodule is, its causes, and possible health implications is essential to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In this article, we will address the most important information related to kidney nodules and how they can affect the health of patients.
An Overview of the Kidneys and Their Functions
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located at the lower back, on each side of the spine. They play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis, that is, the balance of vital functions. Some of the main functions of the kidneys include:
- Filtering the blood: The kidneys remove waste and excess water from the blood, producing urine. They are responsible for filtering about 120 to 150 liters of blood per day, eliminating approximately 1 to 2 liters of urine.
- Blood pressure regulation: The kidneys help regulate blood pressure by controlling the amount of fluids in the body and producing hormones such as renin and angiotensin.
- Electrolyte balance: The kidneys control the levels of minerals in the blood, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, which are essential for the proper functioning of cells and tissues.
- Hormone production: The kidneys produce hormones like erythropoietin (responsible for the production of red blood cells) and calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D), which play important roles in the health of the body.
- pH regulation: The kidneys are also responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance of the body by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate.
As can be seen, the kidneys have a number of vital functions, and therefore, it is important to be attentive to their health and the emergence of possible changes, such as renal nodules.
Throughout this article, we will explore the causes of kidney nodules, symptoms that may indicate the presence of a kidney nodule, and the treatment options available to deal with this condition.
The goal is to provide useful and up-to-date information so that patients and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about the diagnosis and treatment of kidney nodules.
Stay with us and discover everything you need to know about kidney nodules, unveiling the mysteries surrounding this condition and learning to identify and treat potential kidney problems efficiently and safely.
What is a Kidney Nodule?
Definition and Explanation of Renal Nodules
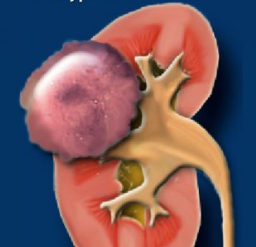
A renal nodule is a lesion or mass that develops in the kidneys, which can be an incidental finding on imaging tests or discovered due to the presence of symptoms. These masses can vary in size and consistency and, depending on their characteristics, can be classified as benign or malignant.
Accurate diagnosis and differentiation between types of nodules are crucial for determining appropriate treatment and ensuring the best possible prognosis for the patient.
Difference Between Benign and Malignant Kidney Nodules
Renal nodules can be classified into two main categories: benign and malignant. Here, we detail the main differences between the two types:
- Benign nodules: These are non-cancerous masses that generally do not pose a significant health risk to the patient. They may be stable, showing no growth over time, or grow slowly. Examples of benign nodules include simple renal cysts, angiomyolipomas, and oncocytomas. Although they usually do not pose a life-threatening risk, some benign nodules can cause discomfort or complications, such as bleeding, depending on their size and location.
- Malignant nodules: These are cancerous masses with the potential to invade adjacent tissues and spread to other parts of the body (metastases). The most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma, which accounts for about 90% of cases. Other types of kidney cancer include transitional cell carcinoma and renal sarcoma. Malignant nodules require more aggressive treatment, such as surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy, and their prognosis depends on the stage at which they are detected.
Prevalence and Incidence of Renal Nodules
The prevalence of renal nodules has increased in recent decades, mainly due to the greater use of imaging tests, such as ultrasonography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging. It is estimated that approximately 20% to 30% of incidental renal nodules are malignant, while the majority are benign.
The incidence of kidney cancer has been increasing by about 2% per year over the past few decades. In 2021, kidney cancer accounted for about 4% of all new cancer cases diagnosed, with approximately 431,000 new cases and 180,000 deaths worldwide.
In Brazil, kidney cancer accounted for about 1.5% of cancer cases in men and 1% in women in 2020.
It is important to note that the risk of developing malignant renal nodules may be higher in individuals with specific risk factors, such as a family history of kidney cancer, smoking, obesity, and high blood pressure.
Now that we better understand what a kidney nodule is and its prevalence and incidence, it is crucial to be informed about the possible causes and conditions related to these renal masses.
In the next subtitle, we will discuss the common causes of kidney nodules, as well as risk factors associated with these conditions. Knowing the causes and risk factors is essential to prevent the development of renal nodules and to ensure early diagnosis and treatment if they occur.
Causes of Kidney Nodules
Simple and Complex Renal Cysts
Renal cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in the kidneys and are a common cause of kidney nodules. Simple renal cysts are generally benign and do not pose a health risk. They can be single or multiple and usually do not cause symptoms, often being discovered incidentally during imaging tests.
In contrast, complex renal cysts have more irregular features and can be classified into different categories based on their malignant potential. These cysts may require more rigorous follow-up and, in some cases, specific treatment.
Benign Tumors
Besides renal cysts, other types of benign nodules can form in the kidneys. Some examples include:
- Adenomas: These are benign tumors that originate in the epithelial tissue of the renal tubules. They are rare and usually small, often being asymptomatic and detected incidentally.
- Angiomyolipomas: These are benign tumors made up of blood vessels, smooth muscle, and fatty tissue. They can occur singly or in association with genetic diseases, such as tuberous sclerosis. Angiomyolipomas generally do not cause symptoms, but in rare cases, they can lead to internal bleeding and pain.
Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors are the most concerning cause of kidney nodules. Some of the main types of kidney cancer include:
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): This is the most common type of kidney cancer, accounting for about 90% of cases. RCC originates in the cells of the renal tubules and is classified into different subtypes, such as clear cell renal cell carcinoma, papillary renal cell carcinoma, and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma (also known as Urothelial Carcinoma): This type of cancer originates in the cells lining the renal tubules and urinary tract. This type of cancer is more common in the bladder but can also affect the kidneys.
- Renal Sarcomas: These are rare malignant tumors that originate in the connective tissue of the kidneys. They account for less than 1% of kidney cancers and include types such as clear cell sarcoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Risk and Genetic Factors
Several risk factors are associated with the development of kidney nodules, especially those of a malignant nature. Some of these factors include:
- Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of kidney cancer, accounting for about 30% of cases in men and 25% in women.
- Obesity: Excess weight is linked to an increased risk of kidney cancer, possibly due to hormonal and inflammatory changes associated with obesity.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure has also been associated with an increased risk of kidney cancer. The exact mechanism of this relationship is not yet clear but may involve damage to the blood vessels of the kidneys.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as trichloroethylene and cadmium, are linked to an increased risk of kidney cancer in occupationally exposed workers.
- Family History: Having a first-degree relative with kidney cancer increases the risk of developing the disease.
- Genetic Diseases: Some genetic conditions, such as tuberous sclerosis and Von Hippel-Lindau disease, are associated with an increased risk of developing benign and malignant tumors in the kidneys.
Knowing the causes and risk factors associated with kidney nodules, it is important to be aware of the possible symptoms and warning signs. In the next subtitle, we will discuss the common symptoms of kidney nodules and how they can be diagnosed and treated.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Nodules
Many kidney nodules, especially smaller ones, do not cause symptoms and are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests.
However, some nodules may cause specific signs and symptoms, depending on their size, location, and characteristics. Some common symptoms associated with kidney nodules include:
- Hematuria: Presence of blood in the urine, which may be visible to the naked eye or only detectable through laboratory tests.
- Back pain: Pain in the lower back or flank, which can be constant or intermittent, depending on the cause of the kidney nodule.
- Abdominal mass: In cases of large kidney nodules, it may be possible to feel a mass or increased volume in the abdominal region.
- Involuntary weight loss and fatigue: These symptoms may be more common in cases of malignant nodules.
- Fever and malaise: In rare cases, kidney nodules may be accompanied by fever and general malaise, especially if associated with an infection.
The Role of Imaging Tests
Imaging tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis and monitoring of kidney nodules. Some of the most commonly used imaging tests include:
- Ultrasound: This is a non-invasive, radiation-free examination that can detect the presence of kidney nodules and help distinguish between simple cysts and solid masses. However, ultrasound may be limited in evaluating complex nodules and determining their malignant potential.
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT is a more detailed imaging test that uses X-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. CT can help determine the size, location, and characteristics of kidney nodules, as well as assess the presence of metastases in other organs if necessary.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is another advanced imaging test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. MRI can be useful in evaluating complex kidney nodules and determining their malignant potential, especially when CT is inconclusive.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Individualized Patient Approach
Early diagnosis of kidney nodules is crucial to ensure the best possible prognosis, especially in cases of malignant tumors. Identifying and treating kidney nodules in the early stages can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment and improve the patient’s quality of life.
An individualized approach is crucial in managing kidney nodules, taking into account factors such as age, medical history, characteristics of the nodule, and patient preferences. Follow-up and treatment can range from simple observation to more aggressive surgical or therapeutic interventions as needed.
In the next subtitle, we will explore the treatment options available for kidney nodules, both benign and malignant, and discuss how the choice of appropriate treatment can influence the prognosis and quality of life of the patient.
Available Treatments
Conservative Treatments
In some cases, especially when kidney nodules are small and asymptomatic, the doctor may opt for a conservative approach. Some conservative options include:
- Active Surveillance: Careful monitoring of the kidney nodule through periodic imaging tests, such as ultrasound, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging. This allows the doctor to track the growth and changes in the nodule over time and intervene if necessary.
- Embolization: In cases of kidney nodules that cause symptoms such as pain or bleeding, embolization can be used to stop the blood flow to the nodule. This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting embolizing substances into the blood vessels that feed the nodule, reducing its size and relieving symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Surgeries
For larger, symptomatic kidney nodules or those suspected of being malignant, minimally invasive surgeries may be indicated, such as:
- Partial Nephrectomy: Removal of part of the affected kidney, preserving as much healthy renal tissue as possible. This procedure can be performed laparoscopically or robotically, minimizing pain and postoperative recovery.
- Total Laparoscopic or Robotic Nephrectomy: Complete removal of the affected kidney, usually indicated for larger or invasive malignant kidney nodules. Laparoscopic or robotic surgery allows for quicker recovery and less pain compared to conventional open surgery.
Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy for Advanced Kidney Cancer
In cases of advanced or metastatic kidney cancer, treatment options include targeted therapies and immunotherapy:
- Targeted Therapies: These drugs work by blocking the growth and spread of cancer cells, affecting specific pathways involved in tumor growth. Examples include tyrosine kinase inhibitors and inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy uses drugs that stimulate the patient’s immune system to fight cancer. Examples of immunotherapy include checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, which help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach in Treating Kidney Nodules
The treatment of kidney nodules should be personalized and based on a multidisciplinary approach involving urologists, oncologists, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals. This collaboration allows for evaluating all available treatment options and selecting the best strategy for each patient, taking into account factors such as age, overall health status, nodule characteristics, and patient preferences.
Efficient communication among members of the multidisciplinary team is essential to ensure that the patient receives the most appropriate and up-to-date treatment. Furthermore, involving the patient and their family in the decision-making process is crucial for achieving satisfactory outcomes and improving quality of life.
In summary, treating kidney nodules requires a careful and individualized approach. Treatment options range from conservative approaches, such as active surveillance and embolization, to minimally invasive surgeries and systemic treatments, such as targeted therapies and immunotherapy, for more advanced cases.
Collaboration among healthcare professionals and active patient participation are essential to ensure the best possible prognosis and quality of life.
Prevention and Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adopting habits that promote kidney health can help prevent the development of kidney nodules and other renal conditions.
While not all kidney nodules can be prevented, adopting preventive measures can reduce the risk and ensure that any issues are detected early.
Lifestyle Tips to Prevent Kidney Nodules and Maintain Kidney Health
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps to dilute the concentration of substances that can form kidney stones and contribute to the development of kidney nodules. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. Avoid foods high in sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars, as they can increase the risk of kidney diseases and other related conditions.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for various renal conditions, including kidney cancer. Losing weight if necessary and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of developing kidney nodules.
- Control Blood Pressure: Hypertension is another risk factor for kidney diseases. Regularly monitor your blood pressure and take steps to keep it within a normal range, such as engaging in physical exercise, adopting a low-sodium diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity helps maintain kidney health, control blood pressure, and prevent obesity. Try to incorporate at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for kidney cancer and other kidney diseases. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing kidney nodules and improve overall kidney health.
The Importance of Regular Checkups and Medical Follow-Up
Regular checkups and medical follow-up are essential for early detection of kidney nodules and other renal conditions. Routine screenings typically include blood pressure evaluations, blood and urine tests to check kidney function, and possible signs of problems.
If you have a family history of kidney nodules, kidney cancer, or other renal diseases, inform your doctor, as more frequent monitoring and specific tests may be necessary.
Furthermore, if you notice symptoms that may be related to kidney nodules, such as back pain, hematuria, or an abdominal mass, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for ensuring a favorable prognosis and better quality of life.
In summary, prevention and adopting a healthy lifestyle are key to maintaining kidney health and reducing the risk of developing kidney nodules.
Drinking plenty of water, following a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, controlling blood pressure, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking are important measures that can contribute to kidney health.
Additionally, it is essential to undergo regular checkups and monitor kidney health with your doctor, especially if you have a family history of kidney diseases or experience symptoms related to kidney nodules. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for ensuring a favorable prognosis and better quality of life.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the topic of kidney nodules, aiming to clarify the main doubts and provide valuable information for patients and medical professionals. By summarizing the key points discussed, we reinforce the importance of knowledge about kidney nodules and appropriate treatment.
Recap of the Main Points from the Article
- Introduction: We discussed the importance of knowledge about kidney nodules and presented an overview of the kidneys and their functions.
- What is a Kidney Nodule?: We discussed the definition of kidney nodules, the difference between benign and malignant nodules, and the prevalence and incidence of these conditions.
- Causes of Kidney Nodules: We examined the types of nodules, including simple and complex renal cysts, benign and malignant tumors, and addressed risk and genetic factors.
- Symptoms and Diagnosis: We presented common signs and symptoms of kidney nodules and the role of imaging tests in diagnosis, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and individualized patient approach.
- Available Treatments: We explored conservative treatments, minimally invasive surgeries, and systemic therapies for kidney nodules, emphasizing the importance of a multidisciplinary approach.
- Prevention and Lifestyle: We provided lifestyle tips to prevent kidney nodules and maintain kidney health, as well as emphasized the importance of regular checkups and medical follow-up.
Reiterating the Importance of Knowledge about Kidney Nodules and Appropriate Treatment
Knowledge about kidney nodules is crucial to ensure that patients receive appropriate treatment and can achieve the best possible prognosis. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and the correct choice of treatment are essential to manage this condition and preserve kidney health.
Awareness of the risk factors and causes of kidney nodules allows patients to take preventive measures and adopt healthier lifestyle habits. Prevention is always preferable to treatment, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing kidney nodules.
Moreover, patient involvement in the decision-making process, along with the collaboration of a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, is crucial to ensure that each individual receives the most appropriate treatment for their needs and characteristics.
In summary, knowledge about kidney nodules, awareness of the importance of early diagnosis, and access to effective treatments are fundamental to improving outcomes and the quality of life for patients affected by this condition. Continuing to educate patients and healthcare professionals about kidney nodules and available treatment options is an important step in combating this condition.