Index
Introduction
The Importance of Understanding the Relationship: Does an Enlarged Prostate Cause Impotence?
It’s common for men to have concerns about prostate health and sexual function as they age. An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a condition that affects many men over the years.
At the same time, impotence or erectile dysfunction (ED) is an issue that can impact the quality of life and emotional well-being. So, does an enlarged prostate lead to impotence? Understanding the relationship between an enlarged prostate and impotence is crucial in identifying the best treatment and prevention approach for both conditions.
Basic Information about the Prostate
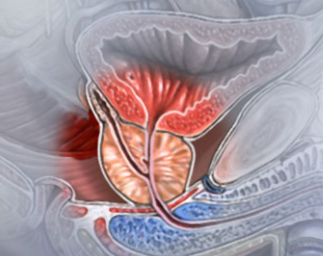
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located beneath the bladder, encircling the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
The main function of the prostate is to produce seminal fluid, which nourishes and protects sperm. This gland is subject to various medical conditions, including an enlarged prostate and prostate cancer.
What is an Enlarged Prostate (BPH)?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that occurs with aging. More than half of men over the age of 50 experience some degree of BPH, and this number rises with age.
Prostate growth can lead to urethra compression, making it hard for urine to flow and causing urinary symptoms like frequent urination, urinary urgency, weak urine stream, and difficulty in completely emptying the bladder.
What is Impotence (Erectile Dysfunction)?
Impotence, also known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
ED is a common problem affecting men of all ages, but it becomes more prevalent as age advances. It’s estimated that about 50% of men between the ages of 40 and 70 experience some degree of erectile dysfunction.
There are various causes of ED, including physical factors like vascular diseases, diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity, as well as psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression. The use of certain medications, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can also contribute to erectile dysfunction.
The Relationship between Enlarged Prostate and Impotence
While an enlarged prostate and impotence are two distinct conditions, they may be related in some cases.
Both conditions are more common in older men, and it’s possible for a man to have both BPH and ED simultaneously. However, this doesn’t necessarily mean one condition directly causes the other.
Studies show that men with BPH are more likely to display symptoms of erectile dysfunction than those without BPH. This might be due to inflammation, hormonal or nerve-related changes connected to prostate growth. Nevertheless, it’s essential to emphasize that BPH itself doesn’t directly cause impotence.
In some cases, medications used to treat an enlarged prostate can have side effects that affect sexual function.
For example, some alpha-blocker drugs, used to relax prostate muscles and enhance urinary flow, can cause retrograde ejaculation, where semen flows back into the bladder instead of exiting through the penis.
Furthermore, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, another type of medication used for treating BPH, might lead to erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and ejaculation issues in some men.
What is an Enlarged Prostate?
Definition of Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common medical condition in older men. BPH occurs when prostate cells multiply, leading to an increase in the gland’s size.
This condition is non-cancerous and does not raise the risk of prostate cancer. However, BPH can cause uncomfortable symptoms and affect the quality of life.
Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
The symptoms of an enlarged prostate vary depending on the degree of growth and the location of the gland. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Difficulty in starting urination
- Weak or intermittent urine stream
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- Need to urinate frequently, especially at night (nocturia)
- Urinary urgency, that is, the sudden and uncontrollable need to urinate
- Urinary incontinence
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Presence of blood in urine (hematuria)
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms isn’t necessarily related to the size of the prostate. Some men with significantly enlarged prostates might have mild symptoms, while others with slightly enlarged prostates may experience more severe symptoms.
Causes of Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
The exact cause of an enlarged prostate isn’t fully understood. However, hormonal changes related to aging are believed to play a key role in the development of BPH.
An increase in estrogen levels and a decrease in testosterone levels might contribute to the growth of prostate cells.
Other factors that can raise the risk of developing BPH include:
- Family history of BPH: Men with close relatives who have the condition are more likely to develop it.
- Ethnicity: BPH is more common in men of African descent and less common in men of Asian origin.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of developing BPH, possibly due to hormonal and inflammatory changes associated with obesity.
- Medical conditions: Men with diabetes, heart diseases, and metabolic disorders might have an increased risk of developing BPH.
How the Enlarged Prostate Affects the Urinary Tract
An enlarged prostate can impact the urinary tract’s function in various ways. Since the prostate encircles the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, its growth can compress the urethra and restrict urine flow.
This compression can lead to several urinary issues, including the symptoms mentioned earlier.
Moreover, an enlarged prostate can cause changes in the bladder and the upper urinary tract. As the bladder works harder to push urine through the compressed urethra, its walls might become thicker and less flexible.
This can result in a decreased bladder storage capacity and an increased feeling of urinary urgency.
In more severe BPH cases, obstruction of urine flow might lead to complications such as urinary tract infections, bladder stones, kidney damage, and even kidney failure.
It’s essential for men experiencing symptoms of an enlarged prostate to consult a urologist to assess the condition’s severity and determine the most suitable treatment.
Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, minimally invasive therapies, or surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms and the individual needs of the patient.
What is Impotence (Erectile Dysfunction)?
Definition of Impotence and Prevalence
Impotence, also known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is a man’s inability to achieve or sustain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse. ED is a common issue, affecting approximately 50% of men between the ages of 40 and 70.
However, the prevalence of erectile dysfunction tends to increase with age, being more prevalent in older men.
It’s essential to emphasize that ED is a treatable condition, and many men can find effective solutions to the issue through consultation with a urologist.
Causes and Risk Factors for Impotence
Impotence can be caused by a variety of factors, which can be classified into psychological, physical, and lifestyle-related. Some of the most common causes and risk factors for erectile dysfunction include:
- Psychological problems: Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship issues can impact a man’s ability to achieve or sustain an erection.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and hormonal disorders, such as hypogonadism, are some of the medical conditions that can lead to ED.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like antidepressants, antihypertensives, and medications to treat an enlarged prostate, can cause erectile dysfunction as a side effect.
- Surgeries and medical treatments: Surgical procedures in the pelvic area, like radical prostatectomy (prostate removal due to cancer), and radiation treatments can impact erectile function.
- Lifestyle factors: Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, obesity, and lack of exercise can increase the risk of developing erectile dysfunction.
The Importance of Seeking Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction
ED can significantly impact a man’s quality of life, self-esteem, and relationships. Additionally, erectile dysfunction can be a warning sign for underlying health issues, such as heart diseases and diabetes. Therefore, it’s crucial for men experiencing ED to seek appropriate medical treatment.
There are various treatment options available for erectile dysfunction, depending on the cause and severity of the issue.
Treatment might include psychological counseling, lifestyle changes, oral medications (like sildenafil), injectable drugs, or vacuum devices. In more severe cases or when other treatment options are ineffective, surgery might be considered, such as the implantation of penile prosthetics.
The first step in treating ED is identifying the underlying cause. A urologist will conduct a comprehensive assessment, including medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, to determine the possible causes of erectile dysfunction and develop a personalized treatment plan.
It’s important to remember that every man is different, and the most effective treatment for erectile dysfunction varies from person to person. With proper guidance from a healthcare professional and commitment to treatment, many men with ED can experience significant improvement in their sexual function and quality of life.
The Relationship Between an Enlarged Prostate and Impotence
Studies and Research on the Relationship Between BPH and Erectile Dysfunction
Numerous studies and research have explored the relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and erectile dysfunction (ED).
Some studies have shown that men with BPH are more likely to experience ED compared to men without BPH. This suggests there might be an association between the two conditions, although the exact relationship is still not fully understood.
How an Enlarged Prostate Might Lead to Impotence
While the precise relationship between BPH and ED isn’t entirely clear, there are various theories that attempt to explain how an enlarged prostate might lead to impotence. Some of these theories include:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the prostate might negatively impact erectile function, as inflammation can cause damage to the blood vessels and nerves involved in erection.
- Nerve compression: Prostate enlargement might lead to the compression of nerves in the pelvic area, potentially affecting erectile function. However, further research is needed to confirm this theory.
- Shared risk factors: BPH and ED share several risk factors such as advanced age, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. These risk factors might contribute to the development of both conditions.
It’s crucial to note that, while BPH and ED might be related, not all men with an enlarged prostate will develop impotence. Similarly, not all men with ED have BPH. The relationship between the two conditions is complex and might vary among individuals.
The Role of Medications and Treatments for BPH in Erectile Dysfunction
Some medications and treatments for BPH might impact erectile function. For instance, alpha-blocker medications, commonly prescribed to address the urinary symptoms of BPH, might cause ED in some men.
However, other studies suggest these drugs might also improve erectile function in certain cases.
Another type of medication for BPH, the 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, has also been associated with ED. These drugs, such as finasteride and dutasteride, work by reducing prostate size but might cause impotence, decreased libido, and ejaculation issues in some men.
Regarding surgical treatments for BPH, like the transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and open prostatectomy, they might pose risks of erectile dysfunction, depending on the surgical technique used and nerve preservation.
However, the erectile dysfunction linked to these procedures is typically temporary and tends to improve over time.
It’s essential for men with BPH and ED to discuss treatment options with a urologist. The doctor will consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and preferences when recommending a specific treatment for BPH and addressing potential side effects on erectile function.
In conclusion, there’s a complex relationship between an enlarged prostate and impotence. While not every man with BPH will develop ED, and not every man with ED has BPH, it’s vital to be aware of the potential links between the two conditions and discuss concerns with a healthcare professional. Furthermore, it’s crucial to consider the impact of medications and treatments for BPH on erectile function when selecting the best therapeutic option.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment Options for BPH and Erectile Dysfunction
There are several treatment options available for men with BPH and erectile dysfunction. The ideal treatment will depend on the severity of the symptoms, underlying medical conditions, and the individual preferences of the patient.
For BPH, treatment options might include:
- Medications: Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are commonly prescribed to address urinary symptoms associated with BPH. As mentioned earlier, these drugs can have side effects on erectile function, so it’s important to discuss options and potential risks with a urologist.
- Minimally invasive therapy: Procedures such as radiofrequency ablation, prostatic artery embolization, and laser vaporization of the prostate can be used to treat BPH with less risk of complications and erectile dysfunction compared to traditional surgery.
- Surgery: Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and open prostatectomy are surgical options to treat BPH in more severe cases or when other treatment options are ineffective.
For erectile dysfunction, treatment options might include:
- Oral medications: PDE5 inhibitors, like sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil, are commonly prescribed for ED. These drugs help relax the muscles and boost blood flow to the penis, facilitating the attainment and maintenance of an erection.
- Hormone replacement therapy: If ED is caused by low testosterone levels, hormone replacement therapy might be a treatment option.
- Psychological therapies: Sex therapy and counseling can be beneficial for men facing emotional or psychological issues contributing to ED.
- Mechanical devices and treatments: Penile vacuum pumps, intracavernous injections, and penile implants are other treatment options for ED.
Addressing Both Conditions Simultaneously
When treating men with BPH and erectile dysfunction, it’s important to address both conditions simultaneously. A urologist might recommend treatments that can help alleviate symptoms of BPH without worsening ED or vice versa. In some instances, successful treatment of one condition might improve the other.
Prevention and Healthy Lifestyle Habits
While not all causes of BPH and erectile dysfunction can be avoided, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help prevent or manage these conditions. Some prevention tips include:
- Maintain a balanced diet: Consuming foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals while avoiding processed and fatty foods can promote prostate health and improve erectile function.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can enhance blood circulation, strengthen the immune system, and prevent weight gain, factors that contribute to overall health and sexual function.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption: Overconsumption of alcohol can increase the risk of developing BPH and also contribute to erectile dysfunction. Limit alcohol consumption and drink in moderation.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for numerous health problems, including erectile dysfunction and urinary tract diseases. Quitting smoking can notably improve overall health and sexual function.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress might contribute to erectile dysfunction and adversely impact overall health. Practices such as meditation, yoga, and therapy can assist in managing stress and enhancing emotional and physical health.
- Have regular medical check-ups: Regular medical check-ups and discussing any prostate or sexual function concerns with a healthcare professional can help identify and address issues early on.
By following these prevention tips and healthy lifestyle habits, it’s possible to reduce the risk of developing an enlarged prostate and impotence or manage these conditions if they are already present.
Consulting a urologist is vital to obtain an accurate diagnosis and discuss the most suitable treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
In this article, we addressed the question of whether an enlarged prostate can cause impotence and explored the relationship between these two conditions. The enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition that affects many men as they age and can cause bothersome urinary symptoms.
Impotence, or erectile dysfunction (ED), is the inability to achieve or maintain a firm erection sufficient for sexual intercourse and is also a common concern among men.
Although the enlarged prostate and impotence are distinct conditions, studies and research indicate that there is a relationship between them. BPH and ED share similar risk factors, such as advanced age, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and cardiovascular diseases.
Moreover, some treatments for BPH, such as alpha-blocker drugs and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, can affect erectile function and contribute to impotence.
However, it’s important to note that not all men with an enlarged prostate will develop erectile dysfunction, and not all cases of impotence are caused by BPH.
Both conditions can be effectively treated, and the ideal treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms, the underlying medical conditions, and the individual preferences of the patient.
For BPH, treatment options include medications, minimally invasive therapies, and surgery. For ED, treatment options range from oral medications to psychological therapies and mechanical devices.
A urologist can guide the patient regarding the most suitable treatment options to address both conditions simultaneously and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and managing stress, can help prevent or manage an enlarged prostate and impotence.
Furthermore, having regular medical check-ups and discussing any prostate or sexual function concerns with a healthcare professional is vital to identifying and addressing issues early on.